No products in the cart.
Description
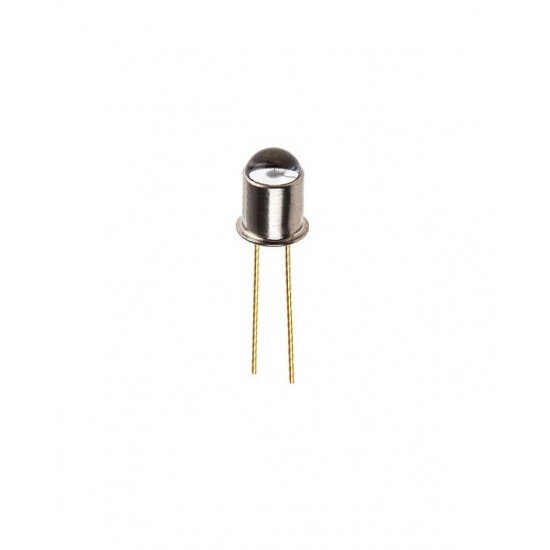
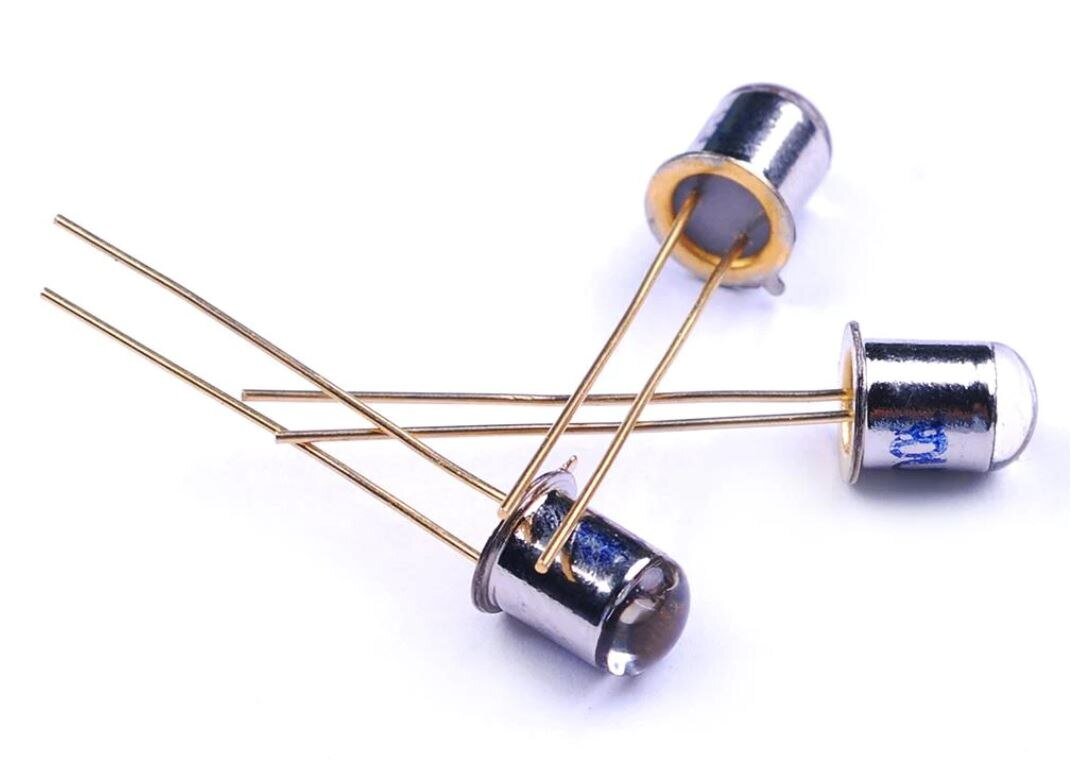
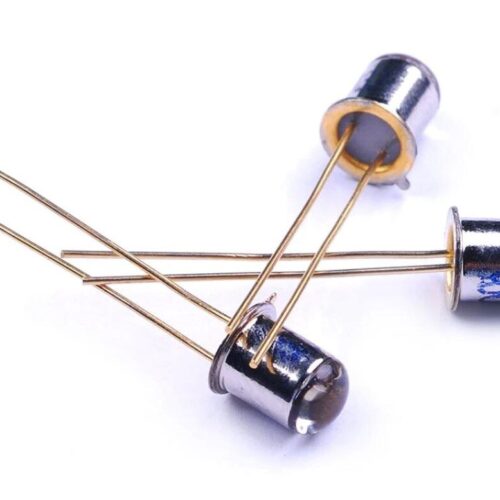
Phototransistor 3DU33
Phototransistor operation
- Photo transistors are operated in their active regime, although the base connection is left open circuit or disconnected because it is not required.
- base of the photo transistor would only be used to bias the transistor so that additional collector current was flowing and this would mask any current flowing as a result of the photo-action.
- For operation the bias conditions are quite simple. The collector of an n-p-n transistor is made positive with respect to the emitter or negative for a p-n-p transistor.
- light enters the base region of the phototransistor where it causes whole electron pairs to be generated. This mainly occurs in the reverse biased base-collector junction.
- hole-electron pairs move under the influence of the electric field and provide the base current, causing electrons to be injected into the emitter.
Specification
- Material: Silicon
- Reverse Breakdown Voltage: 15 VDC
- Maximum Working Voltage: 10 VDC
- Dark Current: 0.3 μA
- Light Current: 0.5 – 1 mA